Learning Algebra
To help with a few of my projects and learning Fusion, I thought I'd brush up on some basic maths - I've been using the Openstax textbooks (access for free at openstax.org) to learn a bit of algebra, trigonometry and geometry. I'm going to record what I've learned here, with an eye on using the Feynman technique to help me understand it.
Classifying Numbers
- Natural numbers
- Whole numbers
- Integers
- Rational numbers
- Irrational numbers
The numbers we use to count real life things {1, 2, 3, ...}
Zero plus the natural numbers {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
Negative and postive whole numbers including 0 {..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
Fractions m/n where m and n are integers and n ≠ 0
Whole numbers can be represented with the whole number as a numerator and 1 as denominator.
A fraction is a ratio. In this sense, irrational means it can't be written as a ratio.
Essentially an irrational number can't be written as a fraction. A clue to this is a non-repeating decimal.
π is an irrational number, it will never fit into a neat fraction. 22/7 is close, but not exactly right.
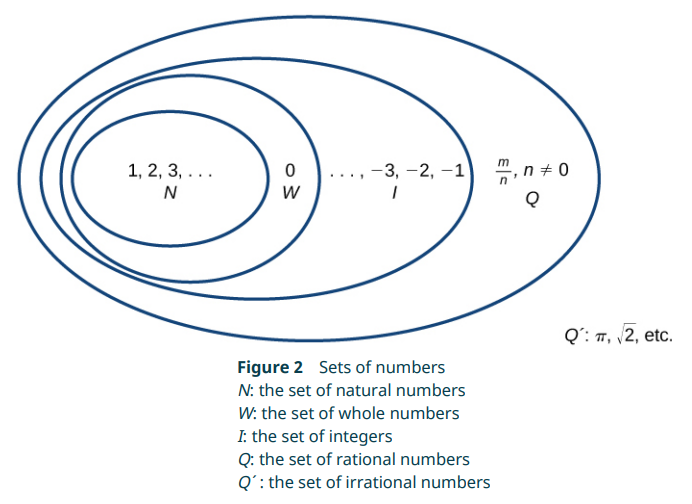
The set of rational numbers contains all of the integers, the set of integers contains the whole numbers, the set of whole numbers contains all the natural numbers. Irrational numbers are those outside the rational set. See diagram below:
PEMDAS
PEMDAS is a mnemonic to help remember the order of operations in algebra.- P - Parentheses
- E - Exponents
- M - Multiplication
- D - Division
- A - Addition
- S - Subtraction
- Simplify any expressions within grouping symbols e.g. (), {}, [], etc.
- Simplify any expressions containing exponents or radicals (see below).
- Perform any multiplication and division in order, from left to right.
- Perform any addition and subtraction in order, from left to right.
Exponents
Exponents are a shorthand way of writing repeated multiplication. For example, 23 is 2 x 2 x 2 = 8.
Radicals
A radical is a root. The square root of 9 is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. The cube root of 27 is 3 because 3 x 3 x 3 = 27.
The radical symbol is the one that people call the sqrt or square root (√) but actually refers to any root and the index number above the radical symbol indicates this. People tend to leave the 2 off when they refer to square root.
More Information
Why these tools?The tools linked above are free, esaily available on the web and are ready to use in the classroom.
Where can I find out more?The worlds of computer graphics, visual arts, creative coding, generative art and other ways of using computers to create art are vast. There is an incredible amount of information available on the web. A great place to start (as with most computing topics) is an awesome list. Here's one for Creative Coding by Terkel Gjervig, designed for beginners.